On Friday, October 1, Nigeria marked its 61st Independence Day anniversary.
It is worth looking back at how far the nation has come and the different socio- economic changes.
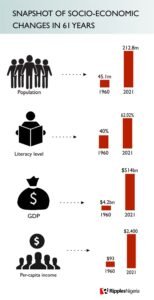
Population
Nigeria’s population statistics have long been contentious, owing to the division between the south and the north, as well as other factors.
However, figures from the World Bank and the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs suggest that Nigeria had a population of 45.1 million in 1960.
Nigeria has not conducted a population census since 2006, thus the National Population Commission depends on the World Barometer estimate of Nigeria’s current population of 212.8 million.
This is a 371.8% growth over the preceding 61 years.
Literacy level
On literacy level, the latest figure from the National Bureau of Statistics shows that the percentage of people who can both read and write, with understanding of a short simple statement about their everyday life, stands at 62.02% .
This is quite a remarkable achievement when compared to the 40% in 1960.
What this means is that at least over 132 million Nigerians can read today in 2021.
GDP
Gross Domestic Product or GDP represents the economic health of a country.
When Nigeria declared its independence in 1960, its GDP was $4.2 billion, the lowest in the period under review.
According to latest figures from the NBS, Nigeria currently has a real GDP of $514 billion.
However, while the nation’s growth since 1960 is certainly laudable, this has unfortunately not percolated into real economic changes in the life of Nigerians.
Per-capita income
Nigeria per capita income as at 1960 stood at $93. However, in 2021 it stands at $2,400.
Poverty Rate
Despite the significant expansion in the economy, the per capita income is not at pace to adequately cater for the country’s population growth.
This imbalance, according to NBS as at 2020 pushed 40 percent or 83 million Nigerians into poverty.
Although Nigeria’s poverty profile for 2021 has not yet been released, it is estimated that the number of poor people will increase to 90 million, or 45% of the population, in 2022.
In contrast, as at 1960, the poverty rate in Nigeria stood at 27 percent.
Inflation
It is easy to find the answer as to why there is a significant increase in poverty in the country.
Inflation, which is the price changes in the goods and services in the country, has accelerated from 5.44% to 17.01% as at the end of August 2021.
Exchange Rate
This increase was even made more significant when you consider that the exchange rate for Nigerian currency to the U.S dollars was N0.71.
As at the end of Thursday trade, on the eve of independence, Naira exchanged to the U.S dollar N413.38 at the official market while at the black market it stood at N570.
Life expectancy
As at 1960, Nigeria’s life expectancy was put at 37 years. In 2021, it stands at 61 years.
In 1960, the male record stood at 36 years while life expectancy for the female was put at 38 years. In 2021, the male figure stands at 59 years while life expectancy for the female gender stands at 63 years.
On Debt
There were no figures for Nigeria’s debt stock from 1960-1979.
However, in the last 41 years, Nigeria’s debt stock has increased from $3.4 billion in 1980 to $86.57 billion as at June 2021.
This is a massive rise by 2446.17% within the period under


















Discussion about this post